ばね形状オブジェクトの生成(three.js)
3次元グラフィックス(WebGL)ライブラリ「three.js」で利用することができるばね型形状オブジェクト(Geometryクラス)を紹介します。
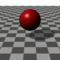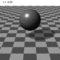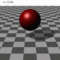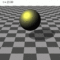
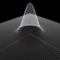
実行例
ばねの全長、ばねの太さ、ばねの巻数などを指定することができます。 また、3次元空間上の2点を結ぶようにばねを伸び縮させることもできます。
ばね形状オブジェクト(SpringGeometryクラス)
ばね形状の詳細な生成方法はこちらを参照下さい。
///////////////////////////////////
// ばね形状オブジェクトの定義
///////////////////////////////////
function SpringGeometry ( radius, tube, length, windingNumber, radialSegments, tubularSegments ){
//Geometryクラスを継承
THREE.Geometry.call( this );
this.radius = radius || 10; //ばねの半径
this.tube = tube || 2; //管の半径
this.length = length || 50; //ばねの長さ
this.windingNumber = windingNumber || 10; //ばねの巻き数
this.radialSegments = radialSegments || 20; //外周の分割数
this.tubularSegments = tubularSegments || 20; //管周の分割数
this.setSpringVertices( this.radius, this.tube, this.length, this.windingNumber, this.radialSegments, this.tubularSegments );
this.setSpringFaces( this.radius, this.tube, this.length, this.windingNumber, this.radialSegments, this.tubularSegments );
//面の法線ベクトルを計算
this.computeFaceNormals( );
//面の法線ベクトルから頂点法線ベクトルの計算
this.computeVertexNormals( );
}
SpringGeometry.prototype = Object.create( THREE.Geometry.prototype );
SpringGeometry.prototype.constructor = SpringGeometry;
//頂点座標の設定
SpringGeometry.prototype.setSpringVertices = function ( radius, tube, length, windingNumber, radialSegments, tubularSegments ){
var geometry = this;
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//(0)必要な変数の準備
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
radius = radius || 1; //ばねの半径
tube = tube || 0.2; //管の半径
length = length || 5; //ばねの高さ
var Nw = windingNumber || 10; //巻き数
var Nr = radialSegments || 10; //外周分割数
var Nt = tubularSegments || 10; //管周分割数
//管断面作成当たりの高さの増分
var deltaH = length / Nw / Nr;
var n = 0;
var v = new THREE.Vector3();
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//(1)ばねオブジェクトを構成する頂点座標の取得
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
for( var w = 0; w < Nw; w++ ){ //巻き番号
for( var r = 0; r < Nr; r++ ){ //外周の分割番号
var phi = 2.0 * Math.PI * r/Nr; //外周の分割番号
//管断面の中心座標のz成分
var h = deltaH * ( Nr * w + r);
for( var t = 0; t < Nt; t++ ){ //管の分割
var theta = 2.0 * Math.PI * t / Nt; //管の分割角
v.set(
( radius + tube * Math.cos( theta) ) * Math.cos(phi), //x座標
( radius + tube * Math.cos( theta) ) * Math.sin(phi), //y座標
tube * Math.sin( theta) + h - length / 2 //z座標
);
if( geometry.vertices[ n ] ) geometry.vertices[ n ].copy( v );
else geometry.vertices[ n ] = v.clone()
n++;
}
}
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//最後の管断面の頂点座標
var w = Nw;
var r = 0;
//管断面の中心座標のz成分
var h = deltaH * ( Nr * w + r);
for( var t = 0; t < Nt; t++ ){
var phi = 0.0;
var theta = 2.0 * Math.PI * t / Nt; //管の分割角
v.set(
( radius + tube * Math.cos( theta) ) * Math.cos(phi), //x座標
( radius + tube * Math.cos( theta) ) * Math.sin(phi), //y座標
tube * Math.sin( theta) + h - length / 2 //z座標
);
if( geometry.vertices[ n ] ) geometry.vertices[ n ].copy( v );
else geometry.vertices[ n ] = v.clone()
n++;
}
//最初の管断面の中心座標
v.set( radius, 0, - length / 2);
if( geometry.vertices[ n ] ) geometry.vertices[ n ].copy( v );
else geometry.vertices[ n ] = v.clone()
n++;
//最後の管断面の中心座標
v.set( radius, 0, length / 2);
if( geometry.vertices[ n ] ) geometry.vertices[ n ].copy( v );
else geometry.vertices[ n ] = v.clone()
n++;
}
//ポリゴン面の設定
SpringGeometry.prototype.setSpringFaces = function ( radius, tube, length, windingNumber, radialSegments, tubularSegments ){
var geometry = this;
var Nw = windingNumber || 10; //巻き数
var Nr = radialSegments || 10; //外周分割数
var Nt = tubularSegments || 10; //管周分割数
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//(2)ばねオブジェクトを構成する面指定配列の設定
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
for( var w = 0; w < Nw; w++ ){ //巻き番号
for( var r = 0; r < Nr; r++ ){ //外周分割数
//巻き番号の指定
var w1 = w;
var w2 = ( r !== Nr -1 )? w : w + 1;
//外周分割番号の指定
var r1 = r;
var r2 = ( r !== Nr -1 )? r + 1 : 0;
for( var t = 0; t < Nt; t++ ){ //管分割数
//管分割番号
var t1 = t;
var t2 = ( t !== Nt -1 )? t + 1 : 0;
//平面を構成する4点の頂点番号の算出
var v1 = (Nr * Nt) * w1 + Nt * r1 + t1;
var v2 = (Nr * Nt) * w1 + Nt * r1 + t2;
var v3 = (Nr * Nt) * w2 + Nt * r2 + t1;
var v4 = (Nr * Nt) * w2 + Nt * r2 + t2;
//頂点番号v1,v3,v4を面として指定
geometry.faces.push ( new THREE.Face3( v1, v3, v4) );
//頂点番号v4,v2,v1を面として指定
geometry.faces.push ( new THREE.Face3( v4, v2, v1) );
}
}
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//最初の管断面の面を指定
var w = 0
var r = 0
for( var t = 0; t < Nt ; t++ ) { //管分割数
//管分割番号
var t1 = t;
var t2 = ( t !== Nt -1 )? t + 1 : 0;
//管断面の中心座標とその他の2点の頂点番号
var v1 = (Nr * Nt) * Nw + Nt;
var v2 = (Nr * Nt) * w + Nt * r + t1;
var v3 = (Nr * Nt) * w + Nt * r + t2;
geometry.faces.push(
new THREE.Face3( v1, v2, v3 )
);
}
//最後の管断面の面を指定
var w = Nw;
var r = 0;
for( var t = 0; t < Nt ; t++ ) { //管分割数
//管分割番号
var t1 = t;
var t2 = ( t !== Nt -1 )? t + 1 : 0;
//管断面の中心座標とその他の2点の頂点番号
var v1 = Nw * Nr * Nt + Nt + 1;
var v2 = (Nr * Nt) * w + Nt * r + t1;
var v3 = (Nr * Nt) * w + Nt * r + t2;
geometry.faces.push(
new THREE.Face3( v1, v3, v2 )
);
}
}
//頂点座標の再設定
SpringGeometry.prototype.updateSpringGeometry = function( radius, tube, length ){
this.radius = radius || this.radius;
this.tube = tube || this.tube;
this.length = length || this.length;
this.setSpringVertices( this.radius, this.tube, this.length, this.windingNumber, this.radialSegments, this.tubularSegments );
//面の法線ベクトルを計算
this.computeFaceNormals( );
//面の法線ベクトルから頂点法線ベクトルの計算
this.computeVertexNormals( );
this.verticesNeedUpdate = true;
this.normalsNeedUpdate = true;
}
ばね形状オブジェクトの生成方法
通常の形状オブジェクトと同様、Meshクラスの引数に与えることで3次元オブジェクトを生成することができます。
//形状オブジェクトの宣言と生成 var geometry = new SpringGeometry( 5, //ばねの半径 1, //管の半径 25, //ばねの長さ 5, //ばねの巻き数 20, //外周の分割数 20 //管周の分割数 ); var material = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial(); //ばねオブジェクトの生成 spring = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material); //ばねオブジェクトのシーンへの追加 scene.add(spring);
ばねの始点と終点を指定
3次元空間上の2点を結ぶようにばねを伸び縮させるためのメソッドを用意します。
//メソッドの追加
spring.setSpringBottomToTop = function ( bottom, top ){
//ばねオブジェクトの底面中心から上面中心へ向かうベクトル
var L = new THREE.Vector3( ).subVectors( top, bottom );
//ばねの中心座標
var R = new THREE.Vector3( ).addVectors( top, bottom ).multiplyScalar( 1/2 );
//ばねオブジェクトの位置を指定
this.position.copy( R );
//ばねの形状オブジェクトの更新
this.geometry.updateSpringGeometry (
this.radius, //外円の半径
this.tube, //管円の半径
L.length() //バネの長さ
);
//ばねの向きを指定
this.lookAt( top );
}
上記の実行例では、描画ステップごとにばねの下底と上底の座標を次のように更新しています。
//下底の位置ベクトル var bottom = new THREE.Vector3( 5 * Math.sin( Math.PI*step/60 ), 0, 0); //上底の位置ベクトル var top = new THREE.Vector3( 0, 5 * Math.sin( Math.PI*step/120 ), 20 + 15 * Math.sin( 2*Math.PI*step/60 ) ); //ばね形状の更新 spring.setSpringBottomToTop( bottom, top );